GIF Quantum LS Imaging Filter
Imaging filter for cryo-EM
Gain fundamental insights into cellular organisation and ultrastructure with the Gatan GIF Quantum LS imaging filter. The system combines high performance energy filtration with direct detection technology. It is ideal for low dose imaging applications. Enhance your cryo-EM (cryo-electron microscopy) and cryo-electron tomography for a greater understanding of complex system functions and disease progression at a molecular level.
- Low distortion optics of GIF Quantum energy filters combined with the performance of the K2 Summit
- Image smaller particles with a DQE (detective quantum efficiency) up to 80% and short exposure times
- High contrast on thick samples with an industry-leading energy filter
- 4-fold increase in field of view
- Fully automated multi-tilt and -region acquisition, for unattended operation
Contact us for more information and quotes:
+44 (0)1223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com

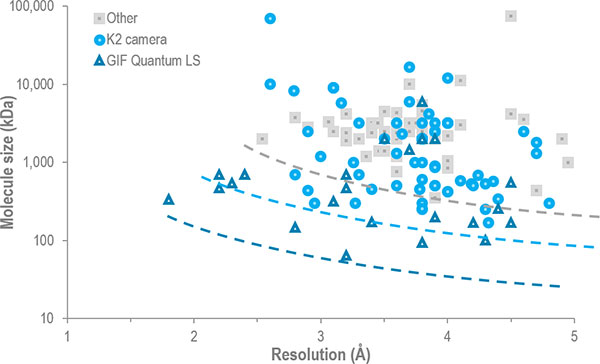
Resolution versus molecule size for published single particle cryo-EM structures. The K2 Summit or Quantum LS were used for every structures at the high resolution frontier across the whole range of molecule sizes.
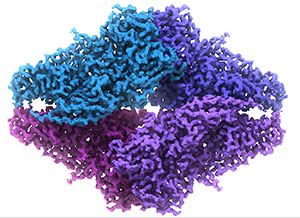
2.2 Å resolution single particle reconstruction of β-galactosidase. Taken using the Gatan GIF Quantum LS imaging filter and K2 Summit camera. Bartesaghi et al., Science 348 (6239): 1147-1151

Escherichia coli β-galactosidase (∼465 kDa) at 3.2 Å resolution. Taken using the GIF Quantum LS energy filter and K2 Summit camera. The first atomic model derived using single-particle cryo-EM analysis closely matches the 1.7 Å crystal structure with a global rmsd of ∼0.66 Å. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 12;111(32):11709-14.

