Bruker Micro-CT Software – New Features of CT-Analyser (CTAn)
Bruker Micro-CT Software: CT-Analyser (CTAn)
CT-Analyser, or CTAn, is a software package for Bruker SkyScan X-ray Micro-CT scanners, for analysis and visualisation by surface rendering. CTAn analyses and processes micro-CT datasets in 2D and 3D for morphometry and densitometry. The software has recently been updated to version 1.15, with a range of new features and improvements.
Blue Scientific is the official UK supplier for the full range of micro-CT scanners from Bruker – if you have any questions or would like advice or quotes, please get in touch:
Contact us on 01223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com
More about Bruker Micro-CT
Faster 3D Thickness Measurement
3D thickness and separation calculation is now 5-8 times faster compared to previous versions of CTAn. An innovative new algorithm subdivides the volume for multi-threading, without compromising accuracy.
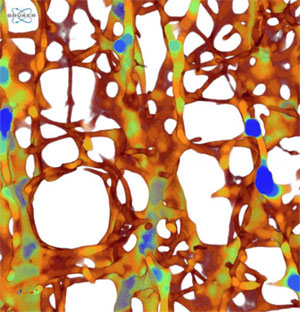
Thickness-colour image. 5-8 times faster spatially resolved local 3D thickness mapping in CTAn.
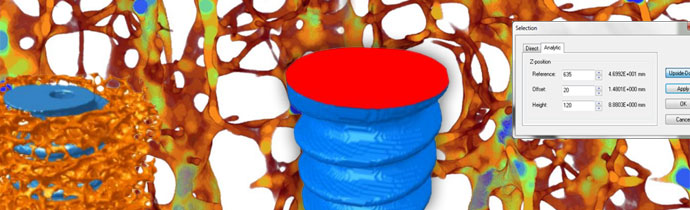
ROI Drawing: Multiple and Subtractive Shapes
Draw multiple ROI (region of interest) shapes using the mouse. You can also subtract shapes, for greater flexibility when examining specific areas. Correct shapes as you need to and create hollow shapes. See below for an example of twin ROI shapes for two molar tooth root canals, and a hollow cortical bone ROI.
Define multiple ROI shapes, for example for both molar root canals (left) and subtract shapes for a hollow ROI, for example for cortical bone (right).
Conditional Mean Filtering
Conditional mean filtering is useful when you defining boundaries between regions of different density. This involves smoothing the reconstructed micro-CT image, but it is important not to compromise the spatial resolution of object boundaries and internal porous spaces. This is where conditional mean filtering is so effective. Neighbouring voxels are smoothed only if their grey-scale difference is less than a certain value (known as “threshold”). Sharp grey-scale gradients at object boundaries exempt them from smoothing. This preserves the detailed architecture of structures, while smoothing less abrupt material gradations.
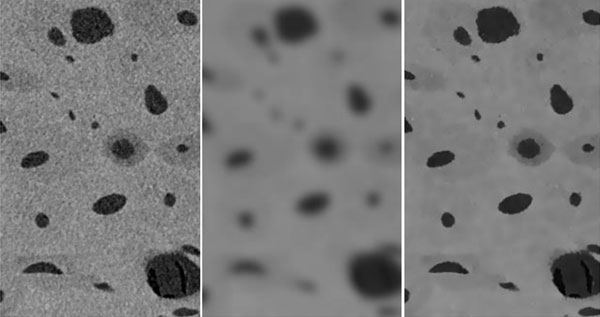
Micro-CT conditional mean filtering. Left: Unsmoothed micro-CT scan of Haversian cortical bone. Centre: Gaussian smoothing. Right: Conditional mean filtered image, with a 5 voxel radius.
Watershedding
This technique separates objects connected by bridges of only a few pixels wide in binarised images, which are discreet elongated objects with roughly circular cross-sections. For example (below), watershedding makes it easier to define separate human hairs in a binarised cross-section, for more accurate analysis.
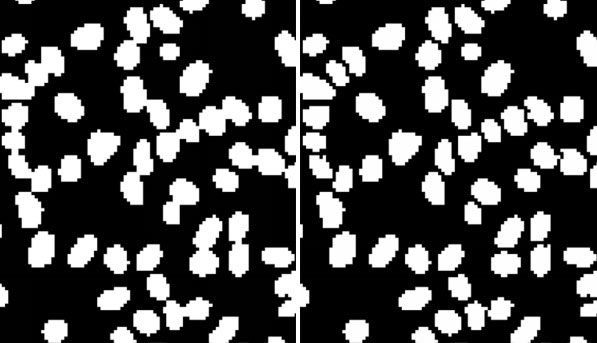
Binarised cross-section through straight hair. Left: Strands in close proximity are fused by pixel connections. Right: Watershedding detects that these are individual strands and shows them as separate objects.
Clearer ROI Reference Level Positioning
The reference level function in CTAn is useful when positioning the selected range relative to a landmark, such as an anatomical location in a biological structure. A new “Upside-Down” button makes it easier to use reference levels when the landmark location is above, not below, the selected range of the cross-section.
Real-Time Results on Screen
Custom Processing and corresponding Batch Manager (“BatMan”) operations are now updated live, in real time on screen. This means you no longer have to wait for the end of a task list to see the outcome of the operations – see the results of each individual plug-in as soon as it is completed.
Quick Custom Task List Selection
In custom processing, task lists can be saved in a new Collections tab, so you can quickly and easily select the task lists you use most often.
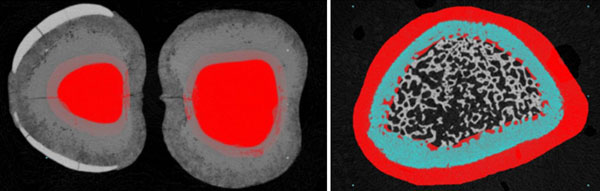
Peripheral Object Area (Exclude VOI Boundaries)
You can now measure an objects surface area, excluding surfaces that are artificially cut in a cross-sectional plane by the top and bottom VOI boundaries. For example, the bone implant contact around an orthopedic implant surface (below). The 2D slice-by-slice analysis measures both intersection surface and object surface, while excluding artificially cut surfaces.
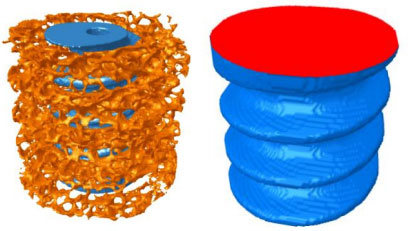
Measuring micro-CT “peripheral area” of objects and of intersection surface, excluding artificially cut surfaces (right, highlighted in red).
Other enhancements
The new CTAn software version also includes a range of smaller improvements to enhance usability and make it quicker and easier to analyse and visualise your micro-CT data:
- Standard deviation of thickness and separation measurements – Now available in summary table reports.
- Colour palette adjustment – As well as customising the cross-section image appearance, you can choose whether or not to apply the same colour change in the projection window (spr image) and the volume rendered image window on screen.
- Bone mineral density calibration – Easily check the date and time of the last bone mineral density (BMD) calibration.
- Easily reset window layout – Quickly and easily reset the CTAn window layout with just one click.
- Quickly select datasets in batch manager – Simple tickboxes to select and deselect.
- Ridler-Calvard auto-threshold – Additional method to complement the existing Otsu thresholding.