Measuring Adhesion in 2D Materials with AFM
A scientific paper has been published in Advanced Materials about studying adhesion in 2D materials with AFM, using the Bruker MultiMode 8.
The paper is by Jonathan M. Polfus, Marta Benthem Muñiz, Ayaz Ali, Daniel A. Barragan-Yani, Per Erik Vullum, Martin F. Sunding, Takashi Taniguchi, Kenji Watanabe and Branson D. Belle. The full paper available online on the Advanced Materials website.
Interlayer Coupling of 2D Materials
The interlayer coupling between 2D materials is of great importance for a fundamental understanding of these systems. It’s also of great significance to the development of transfer techniques for the fabrication of vdW (van der Waals) heterostructures.
However, a great deal is still unknown about their adhesion characteristics, because of the elusive nature of adhesion interaction measurements.
Effects of Temperature on Adhesion
It is thought that intrinsic ripples in 2D materials may cause temperature dependence in adhesion, even though vdW interactions are essentially temperature-independent.
In this paper, adhesion is directly measured between:
- Reduced graphene oxide – coated by solution deposition on AFM tips.
- Graphene, h-BN and MoS2 – supported on SiO2 substrates and as freestanding membranes.
In-situ nanomechanical characterisation revealed a prominent reduction in adhesion energies with increasing temperature. This is ascribed to the thermally induced ripples in the 2D materials.
Measuring Adhesion Forces
Adhesion forces were measured using quantitative nanomechanical mapping (QNM) in PeakForce tapping mode on a Bruker Multimode 8 AFM with sample heating and cooling capabilities.
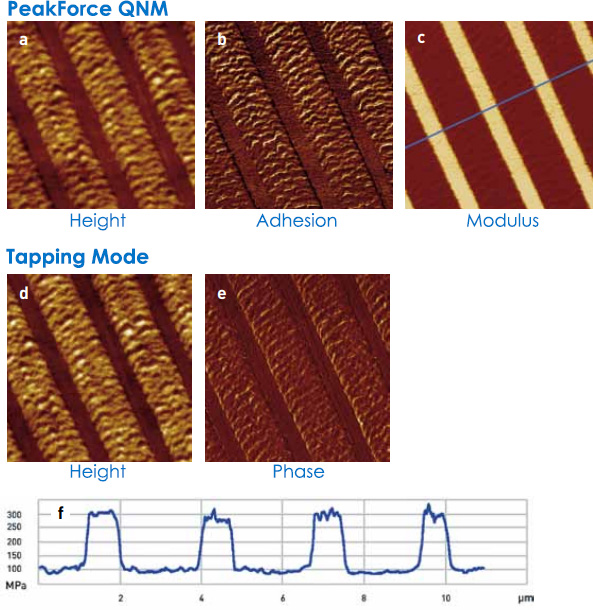
Bruker’s PeakForce QNM mode maps and distinguishes between nanomechanical properties including modulus, adhesion, dissipation and deformation. It delivers atomic resolution in topography and property channels. The method is non-destructive to both tip and sample. Force distance data is analysed directly, so there’s no ambiguity about the source of image contrast, as is often the case with other techniques.
More about mapping surface adhesion properties with PeakForce QNM and new Ringing Mode…
PeakForce QNM brochure
Heating and Cooling
Bruker’s environmental control package opens up new research possibilities. Samples can be heated and cooled between -35°C and 100°C in either air or fluid. A high-range option is also available for temperatures up to 250°C, which is often used to study polymer phase transitions. A unique feature of the package is that you can perform both gas purging to prevent sample oxidation and tip heating to prevent tip contamination.
Scientific Paper in Advanced Materials
The full paper is available to read online on the Advanced Materials website:


Bruker MultiMode 8
- High resolution AFM for small samples.
- Easy to achieve high quality results.
- 6x faster imaging in air than most conventional AFMs.
- Wide range of modes.
- Image in air and fluid, and a variety of temperatures
More Information
Blue Scientific is the official distributor of Bruker AFM in the Nordic region (Sweden, Finland, Norway, Denmark and Iceland). We’re available to answer all your questions – just get in touch:


